Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease Website Course
Evaluating Liver Test Abnormalities
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Liver Disease
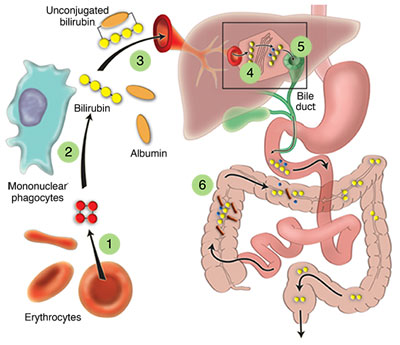
Bilirubin Metabolism
- Heme, the substrate of bilirubin, is derived from red blood cells that have died.
- Heme is degraded to biliverdin by heme oxygenase in the mononuclear phagocytes.
- Biliverdin is subsequently reduced to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase.
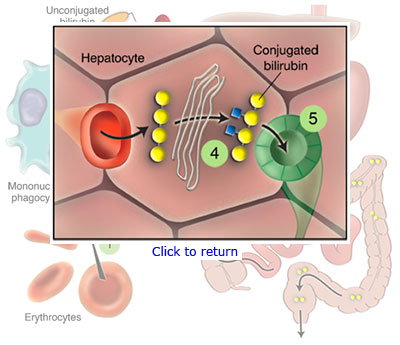
- Circulating bilirubin (insoluble) is bound to albumin and subsequently taken up by the hepatocytes.
- To make it soluble, bilirubin undergoes conjugation, a reaction catalyzed by bilirubin UDPglucuronyl transferase (UDPG).
- Conjugated bilirubin (soluble) is excreted into bile and reaches the bowel.
- Bilirubin glucuronides are deconjugated by colonic bacteria and eliminated in the feces.